- Home
- Toys
- E-Learning
- Retro Mechanics
Who carries heavy loads around today? Who drills a hole in the wall with pure muscle power? Who still washes his clothes on a washboard? Almost nobody. The human being has invented many devices, which make his life and work easier. This began with the work mill for a mill and moved on to the jet engines for a Jumbo jet and then to the computer. Devices that make your work easier or even do it for you are called machines in the technical language.

Machines can:
Examples
Mechanics has to do with effects and forces, which affect rigid and moving bodies. Mechanics is divided into various areas such as statics, dynamics, kinetics or thermodynamics. We will limit ourselves to two areas: dynamics and statics.
Even in the ancient world, scientists studied the areas of mechanics. The old master builders of cathedrals built higher and higher churches that pushed the experimentation with the balance of forces to its limits. Today, a structural engineer does the calculations for the stability of a building. His profession comes from the mechanics subarea of statics. You will learn more about this in the statics part.
Whenever machines or gear units are set in motion, they are dynamic. Dynamics describe the change of the movement variables, for example, for the rotation of a shaft, back-and-forth movements or the toothed gear transmission. So dynamics is the science of changes in movements. You will learn exactly what this is in the following chapters.
The Electric Motor
A motor is a possible drive for a machine. There are two types of motors: the combustion motor and the electric motor. For example, a car is driven by a combustion motor. Of course, you don't have such a complicated motor in your construction kit, but you do have an electric motor, which we will call the E-motor for short.
Electric motors are the drives for most of the everyday machines. They can be used everywhere where electrical energy is available. The electric motor in your construction kit has a very high number of revolutions per minute (RPM), which means that it rotates so fast that you cannot even see one single revolution. But your motor is very ”weak,” which means that it cannot lift loads and cannot drive any vehicle. To reduce the revolutions and the make the motor ”stronger,” you need a gear unit.
Worm Gear Pair
A worm gear pair is best suited to reduce the high RPM of the motor. To do this, a worm gear is placed on the motor shaft, that is the rod, which extends out of the motor casing. The worm gear drives a toothed gear.
This type of gear unit is used where high revolutions per minute are to be reduced in a small area. A worm gear pair works in a self-locking manner, which means that the worm gear can be driven by the worm gear pair, but on the other hand it locks the gear unit.
Worm Gear Pair in a Bar
Bars and cranes use this gear unit because here the safe locking of the worm gear keeps the bar or the attached load from ”reversing” the drive.
Your task:
Of course, you had to turn the crank a few times to move the bar 90°. Were you able to pull the bar down?
See, this is how a self-locking gear unit works. With the small crank, you could easily lift the big bar so you increased the driving force with the worm gear pair.
The worm gear pair has many advantages:
Turntable
The mechanism of the worm gear is used in many machines. A simple example of this is the turntable, your next model.
For this model, the revolutions per minute will be reduced and the direction of rotation will be changed. The resistance of the loaded turntable must not stop the motor.
Your task:
In this chapter, you will learn more about the gear units with toothed wheels.Toothed wheels are among the
oldest and most robust elements of a machine. There are various types and sizes. You know a function similar to toothed gearing from your bicycle. But here the toothed wheels are replaced by chain sprockets and a chain.
Using toothed gearing, you can transmit and change rotational movements. Toothed gearing can:
Crank gears
In the following models, you will build toothed gearing with straight toothed cylindrical gears. Cylindrical gears are used if the rotational motion is to be transmitted to a parallel shaft.
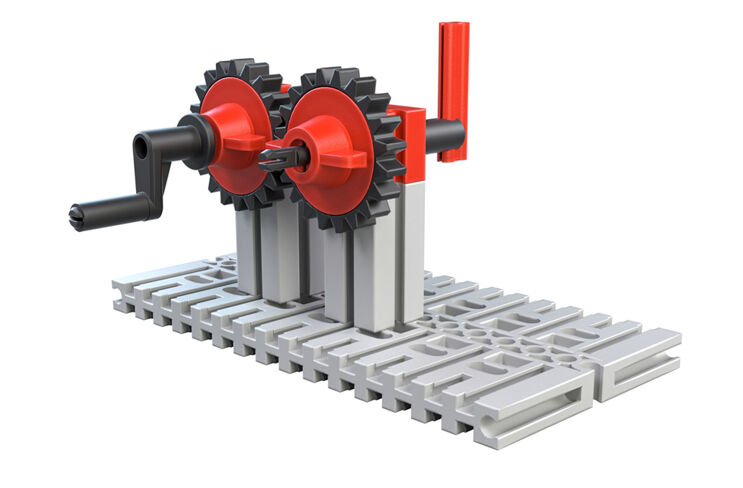
Your task:
If you want to move a vehicle in this way, you would move very slowly. Also, you would go backwards. This model is only to show you how to build a simple gear unit and make calculations for the gear unit.
Your task:
If you would move a vehicle in this way, you would move somewhat faster than with your first model. Calculate the transmission ratio for this gear unit as well.
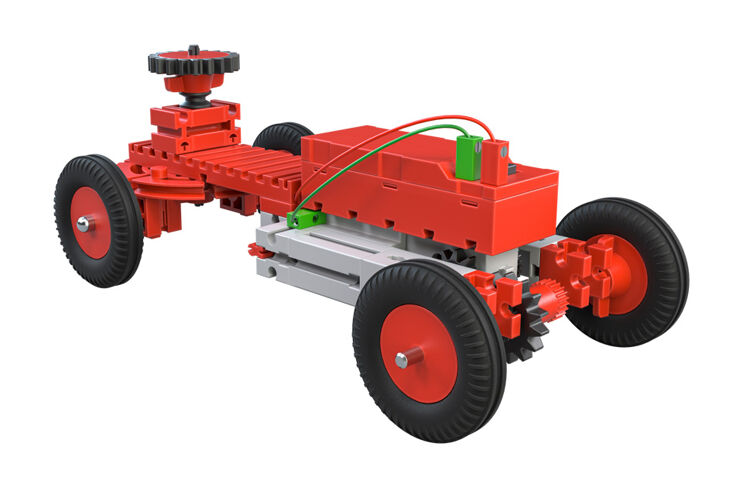
Vehicle Drives
Now you have already learned a lot about gear units and you can try out this knowledge on a model. Build
vehicle 1. With the motor and the gear unit you now have a real vehicle drive.
So that you can go even faster, build a copy of vehicle 2. Now your mobile travels 1.5 times as fast as the one before. But this transmission ratio has its problems on a mountain.
Vehicle 3 has a ”reversed” gear unit construction compared to vehicle 2. How does its speed change in comparison to the other models?
With the three toothed gearings, you have created a transmission ratio of 1:1 with the same revolutions per minute and the same torque. Your second model has a transmission ratio of 1:1.5 and a reduced torque. This means that it is faster but has less ”force.” Vehicle 3 has a transmission ratio of 2:1 and goes slower than the other two and that's why this is called a reduction ratio. This type of transmission has the advantage that it is ”stronger,” meaning it has a higher torque. This effect is used, for example, with a tractor. If travels slower than a car of course, but it has much more power.
You know all three gear unit transmission ratios from your bicycle gear shift. In the front you drive the large wheel and in the rear the small gear pinion to travel faster on the level. But on a mountain you certainly shift to a smaller transmission ratio such as 1:1 or when it is really steep to 2:1.
Toothed Gearing with Chains
If there is a greater distance between two shafts, then a tension gear unit is used to span this distance. Belts or chains are used as a tension medium. They connect the drive gear and the driven gear over longer distances with each other by keeping the machine parts in a certain interaction.
You have such a gear unit on your bicycle. The distance between the pedal drive and the rear wheel is covered by a chain. On a mountain bike or a racing bike, of course you have not only one gear, but you can choose from many gears. This means that you adjust your speed depending on the force needed and the force to be transmitted and the revolutions per minute. In this case, your toothed wheels are not called cylindrical gears, but chain sprockets.
Install the motor in your vehicle with a chain drive. This is exactly how the transmission is done with a moped or motorcycle. Of course, you can now build your own motorcycle from your fischertechnik parts.
Your task:
Vehicle with Steering
The different models showed you how important the right toothed wheel ratio is for the various vehicle types and speeds. So that your vehicle doesn't have to travel in only one direction, it will get steering. Build the vehicle model with steering.
This steering is the simplest and the oldest that human beings have developed. This is called fifth-wheel steering. The Celts developed this for their wagons so they could steer the front axle and so to make the vehicle steerable. They invented the fifth-wheel steering, which is still used today for many trailers, hand carts and horse-drawn wagons. The fifth-wheel steering is a steering system with a stool-like carrier for the axle and the wheels. This is attached to a rotatable pin in the wagon structure such as the base plate or the chassis. The steering system can be controlled either through an extended pivot pin as a steering column or with a rod, the tongue of a wagon, which is attached to the fifth-wheel. In a soap box the fifth-wheel steering can be operated with your feet or with two ropes.

Gearbox with several gears
With the following construction, you expand the simple toothed wheel transmission with gear changing with several gears. This is how a gear unit is developed such as in an automobile, a drill or a moped. This model has a compound gear unit, which means a gear unit, which consists of more than two toothed wheels.
Experiment with the transmission effect of toothed wheels and pairs of toothed wheels placed in a series one after the other.
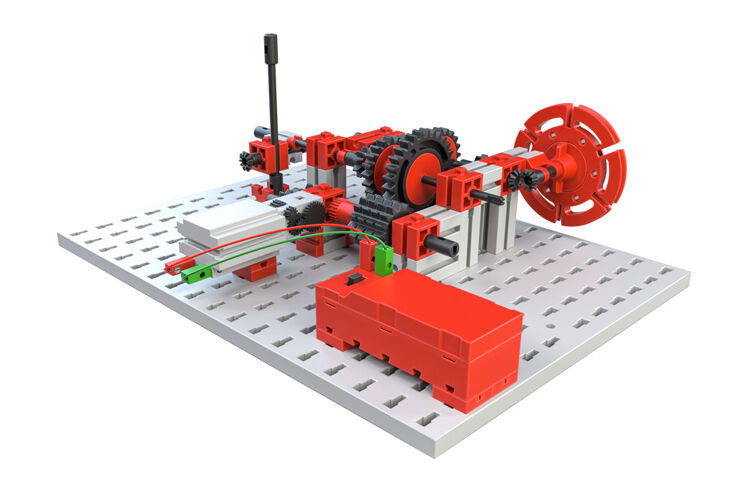
Your task:
This gear unit in gear 3 goes in a different direction than in gear 1 and gear 2. This is because that here, three toothed wheels are in a series.
When an uneven number of toothed wheels are in a series, then the driven gear has the same direction of rotation as the drive gear. This effect is used for a car to drive backwards.
Other experiments:
The Planetary Gear
A planetary gear is a very complex system with various toothed wheel types. It is used in many areas, for example, as a stirrer in a kitchen appliance or as an automatic transmission in a car.But, there the construction is somewhat more complicated.
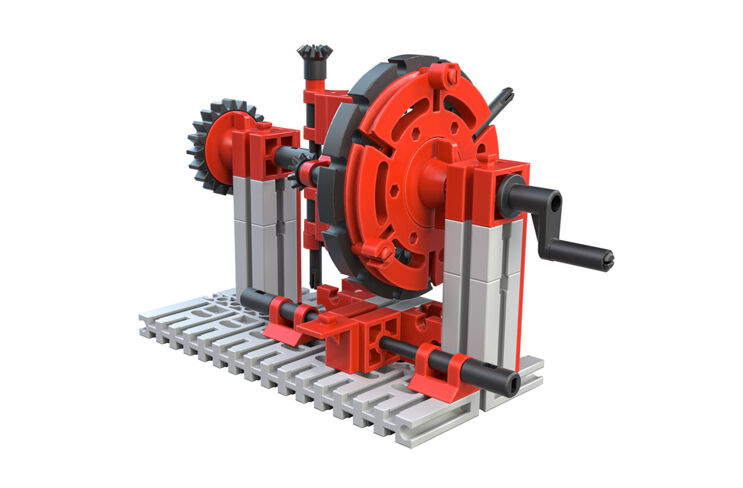
Your task:
Using the slider, that is the name of the lower part of the lever for your model, you can stop the planet carrier or the hollow wheel so that one of the two parts cannot rotate.
The purpose of a planetary gear is simple. It allows the change of the transmission ratio under load, which means without separation of the flow of force between the drive and the driven gear. Due to the internal toothing of the hollow wheel, the toothed wheels are arranged in a particularly compact manner. For the reverse gear for a planetary gear, no additional shaft with a reverse idler gear is necessary.
In the simplest case, the planetary gear consist of the sun gear, planet wheels, the planet carrier and the hollow wheel. For this simple planet wheel set, a sun gear in the middle is connected form-closed by means of several planet wheels with an internally toothed hollow wheel. The sun gear, planet carrier or the hollow wheel can drive, be driven or stalled. To try out your gear unit properly, you have the slider.
Without an additional toothed wheel, by stalling the planet carrier you can adjust the gear unit so that the output is done one time through the planet carrier and one time through the hollow wheel.
This process is used in vehicle technology to shift into reverse gear. To do this, the drive (the crank) must be connected with the sun gear and the axle drive with the hollow wheel.
Your task:
Bevel Gear Unit
With the bevel gear, you can learn how a simple toothed wheel transmission works.
Your task:
This gear unit only changes the direction of rotation by 90°, but the revolutions per minute and torque remain the same.
Kitchen appliance
This model combines the bevel gear unit and the planetary gear. Build this model according to the construction instructions. The fischertechnik stirring device is a model for real pros. Do you know all toothed wheels and types of gear units that are interacting here?
You can make very interesting variations with this model. Modify it according to your imagination. You can put a cup on the base and stir the contents

Differential gear
A differential is always needed, for example, for a multitrack vehicle such as a car when several wheels on an axle are driven. Differentials have two purposes: the distribution of the drive power to two axles and the compensation for the difference in revolutions per minute between these branches.
With this function, the differential is used at two locations:
Your Task:
Rebuild the gearbox model.
Observe how the speed, direction of rotation and torque change in this model. To do this, alternately hold one and the other output gear, then the rotating body (the holder for the center bevel gears) in the middle.
Note your observations in the table:
Car jack
There are situations where you have to lift heavy loads alone. For example, a flat tire. Just imagine that you would have to lift a whole car to change a tire. Of course, you can’t do that. That’s why a car has a car jack. Anyone can do this with a jack. The trick is a screw spindle. This has characteristics similar to the worm gear, which you have already learned about.
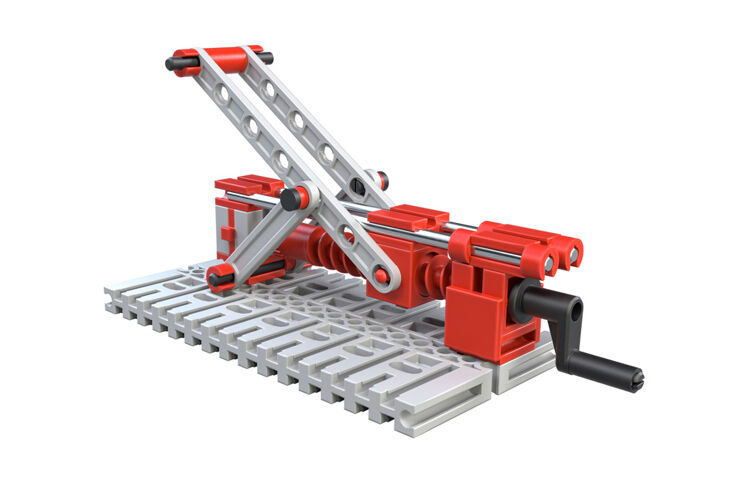

Your task:
To put the lifting arm in a vertical position, you had to turn the crank several times. You certainly saw that the lifting arm cannot be pushed downwards!
A screw spindle mechanism has many advantages:
Scissor elevating platform
The scissor elevating platform shows you how to transform a rotational movement into a parallel up and down movement with the help of a screw spindle, joints and levers.
Your task:
The screw spindle moves the worm nut back and forth. Through the joint, this movement moves the platform up and down. Since the pivotal center for both joints is in the common center, the lifting, that is the up and down movement of the platform, runs parallel to the screw spindle. Both joints move the same distance like scissors. That’s why it is called a scissor elevating platform.
Lathe
This model has two spindle drives. The fischertechnik lathe is a model for real pros. Here, two spindle drives interact. Can you imagine why the lathe has two separate spindle drives?
Coupler Mechanism-Windshield wiper
Do you really know how a windshield wiper works? The next model shows you how it works. Here, a rotational movement is transformed into a back-and-forth or oscillating movement.
To do this, you need a crank or a cam disk. This gear unit is called a crank-rocker gear unit. It transforms a rotational movement into a straight line movement.
Four-bar chain
The four-bar chain consists, as the name implies, of four joints, that is points, at which something can rotate.
Your task:
The frame is rigid and absorbs the movements. The crank must be able to make entire revolutions and the connecting rod transfers the movement of the crank to the gear rocker. The gear rocker only moves in an arc because it is fastened to the frame.
In order that the gear unit can work, the lengths of the four components of the crank gear rocker must be in a certain relation to one another.
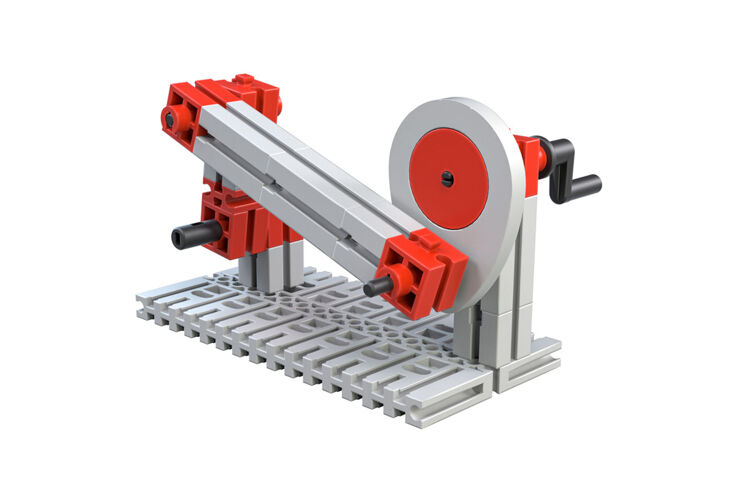

Hackaw Machine
The effect of the crank gear rocker is used in other areas. For a long time, the power hacksaw machine was a big help for the metal construction builders. Its simple construction helps you to better understand a coupler mechanism.
With this type of gear unit, a rotational movement is transformed into a straight-line back-and-forth movement. The end points, where the saw cannot go any farther, are called the dead center points.
Your task:
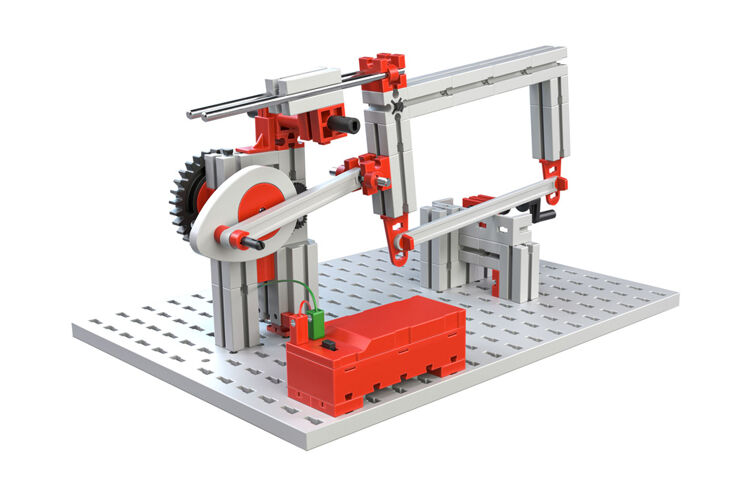
Lever
Four thousand years ago, to determine the price of an item, the quantity of the item was compared to weights. This was done using a beam and scales, with which the balance of forces of two weights was measured. For your model, this is a beam attached at the mean pivotal center and the beam has a bowl at each end. Both indicators in the middle of the weighing beam must be in line when the forces are balanced.
These scales work according to the principle of levers of equal length. A lever is a straight beam, which is attached in a manner allowing it to rotate and on which two forces act. The distances between the application points of the forces and the pivotal center are called the lever arms.
Both sides beside the pivotal center are of equal length and equal weight. You know the principle of these scales from a teeter-totter. To have the levers in balance, the weights on the levers and their distance from the pivotal center of the scales must be the same.
Your task:
Scales with Sliding Weight
You have to have a bit of patience to find two weights that have exactly the same weight. That’s why a further development of the beam and scales is scales with a sliding weight.
These scales also work according to the principle of levers of the same length, but here torques are used as a sort of trick. Both sides beside the pivotal center are the power arms. The further to the outside that a weight hangs on a power arm, the higher its force. With the help of the slider, the torque on a power arm can be changed. The arm with the weighing bowl is called the lift arm.
Your task:
To put a lever in balance, the sum of the counter-clockwise torques and the sum of the clockwise torques must be equal. This sounds complicated, but it is really not that difficult. The law says that both arms to the left and right of the pivotal center have to have the same weight, but not that they have to be the same length. The farther away a weight is from the pivotal center, the greater the force of the lever and so its weight as well
Lifting tackle with 2 rope pulleys
Your task:
Lifting tackle with 3 rope pulleys
Now that you know how a lifting tackle works, you can build a lifting tackle with four rope pulleys. In addition, a motor will be installed to replace your force.
Lifting tackle with 4 rope pulleys
Your task:
To be able to lift heavy loads with little force, you need lifting tackles with two, four or six pulleys. If the weight of the pulleys and the frictional forces are neglected, the lifting tackle reduces the force, depending on the number of pulleys, to one-half, one-fourth and one-sixth. For this lifting tackle, the motor must only lift one-fourth of the load.
However, this does have a disadvantage: when the load is lifted 10 cm, how far must your motor roll the rope up.
Y 10 cm Y 20 cm Y 30 cm Y 40 cm
Physics understands the way your lifting tackle works and has invented a law for this and this law is called the ”Golden Rule”. It states: ”Work cannot be saved, whatever is saved on force, must be added in time and distance!”
Statics studies conditions, under which the forces acting on a body are in balance. This makes statics the basis for all calculations and designs of constructions such as bridges or houses.
Various forces act on components of statics. The weight of a construction is called dead weight. The weight of people, furniture, plates or even cars is called traffic load.
Table
Your table is also a statical object. It carries its own weight, that is the dead weight, and the traffic loads as well. These are plates, cups, food or drinks, which are on the table, but this also includes accidentally bumping into the table.
So that a table can handle all of these loads, it needs a lot of statical specialties.
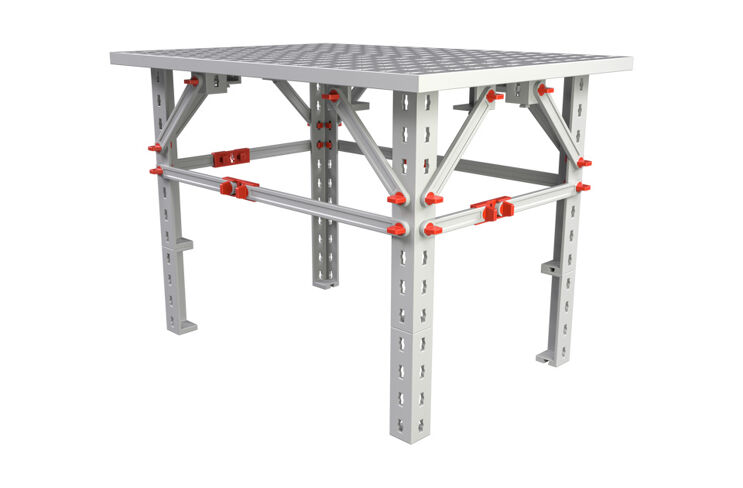

Your task:
Your second task:
Double Ladder
The double ladder has a very simple statical construction. It also has angled legs with strut bracing.
The strut braces serve as rungs for the ladder. The double ladder consists of two individual ladders, which are connected at a pivotal center at the top. In addition, there is bracing of both ladders in the lower part.
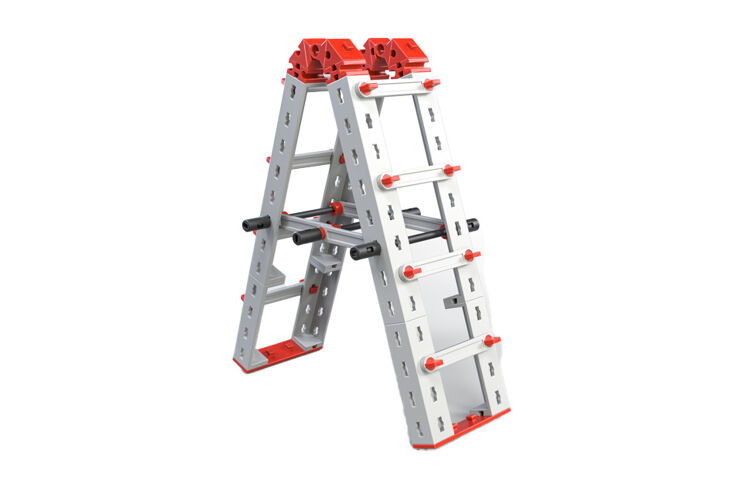

Your task:
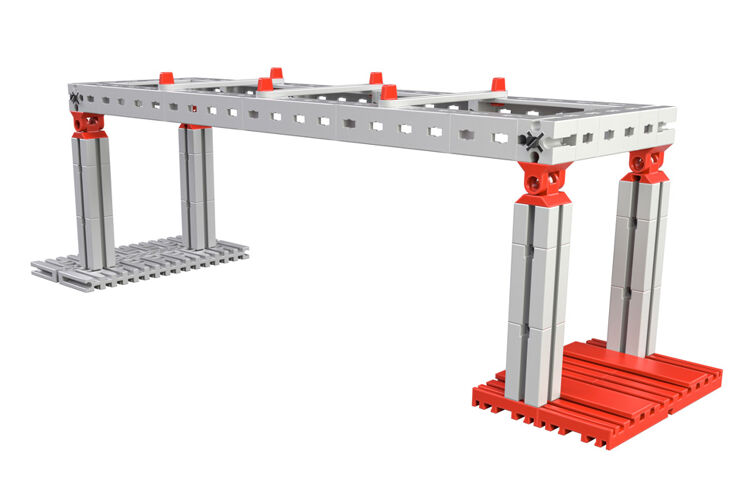
Girder Bridge
An optimal bridge has four characteristics: it is safe, long, cheap and looks good. With your first bridge model, you will get to know a classic of bridge building.
Your task:
This one-field girder bridge is excellently suited for low loads and small span lengths. It fulfills all requirements. However, if the distance between the supports is greater, the bridge loses its stability
Bridge with Underbeam
The bridge with underbeam reminds one of suspension bridges, which spann wild gorges. But this bridge has almost nothing in common with the design of a suspension bridge. You will find out why this is so during experiments with the model.
Your task:
From the load experiments, you certainly found that your bridge is very stable and can withstand large compressive forces. The bridge with underbeam functions due to its trussed construction. This type of construction is suited for large loads, but not for big span lengths. The greatest span lengths are reached with suspension bridges, but they cannot withstand such great forces. The bridge with underbeam and the suspension bridge only look similar. From a statics viewpoint, they are completely different.
Bridge with Upperbeam
An upper boom (upperbeam) bridge can have significantly longer span lengths and withstand significantly greater loads. This bridge also has a trussed design. Strut braces, braces and statical triangles stabilize this bridge.
Your task:
This bridge form can withstand bigger loads than the girder bridge. The compressive force is now transmitted not only to the girder, but is also distributed to the additional components. The upper boom consists of crossed diagonals, which are attached at the upper nodes of the side elements. The diagonals on the upper boom prevent the twisting of the bridge. If the strut braces project upwards, then this bridge design is called a truss frame.
High Hunting Stand
If you want to move up then the high hunting stand is exactly what you need. The statical basis for this is the framework, which is the area joining of triangles.

Your task:
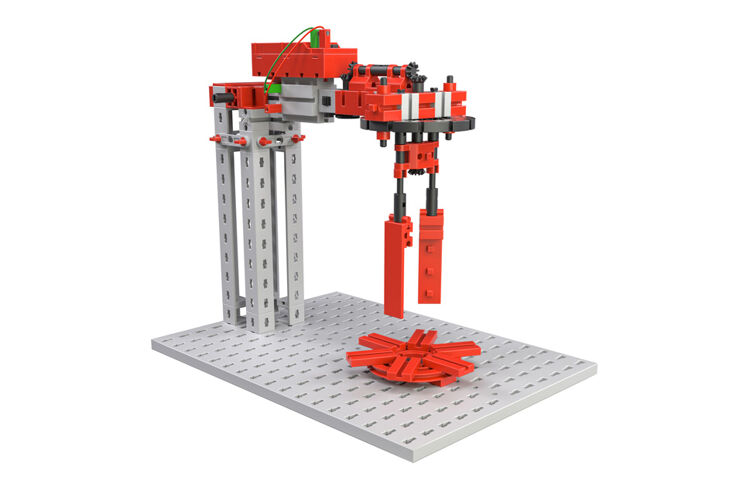
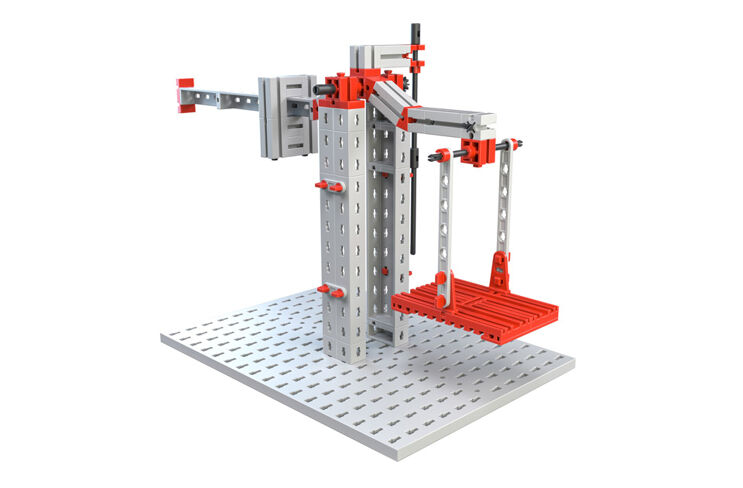
Crane
You were able to gather experience from the areas of mechanics, levers and statics with the previous models. The final model will integrate this experience. The crane allows you to recognize the interplay of components and assembly groups and to test the statics for their load carrying capacity.

Your task:
There are several types of gear units available for lifting weights.
The crowning element for your model is the use of a lifting tackle.
